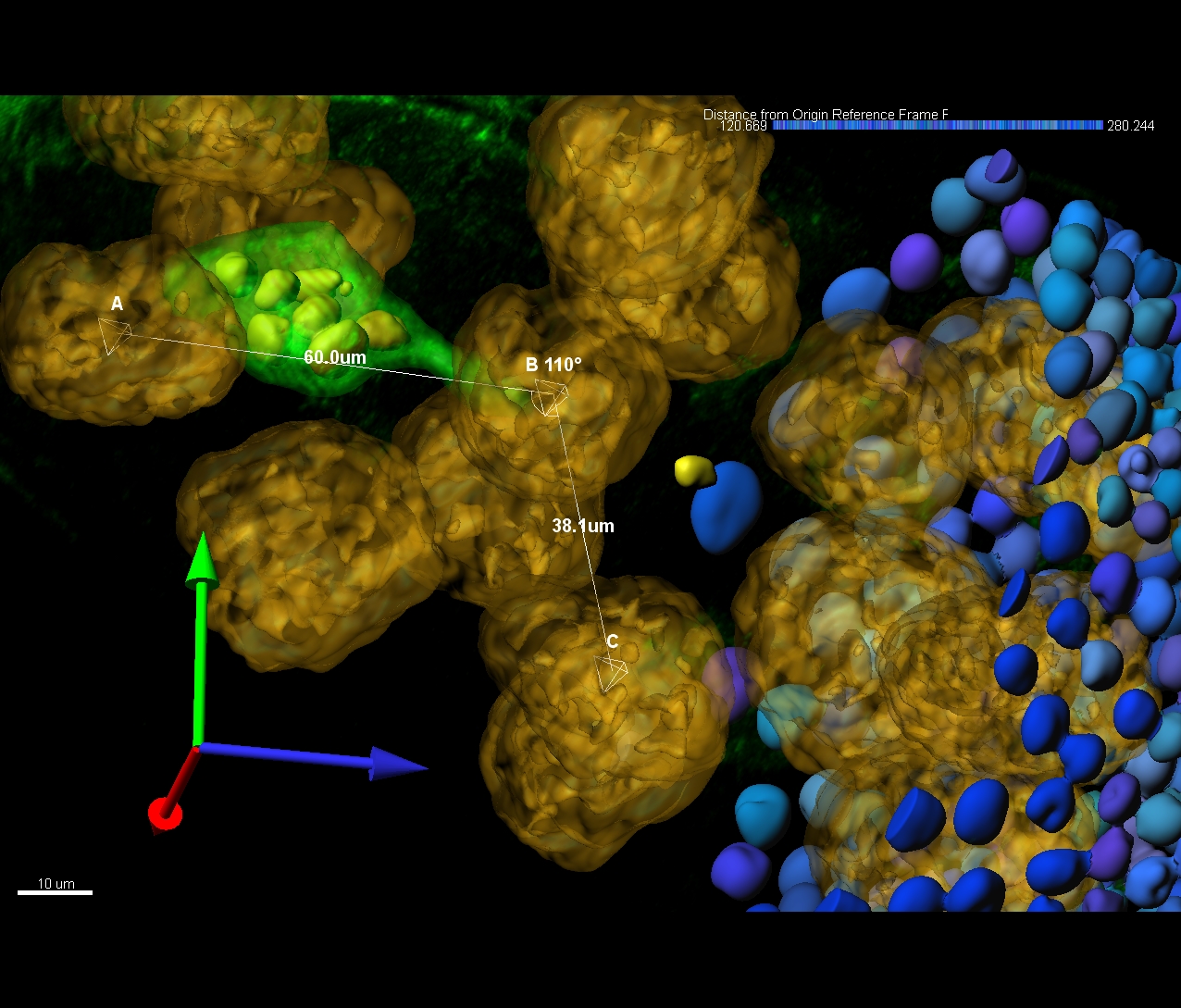
- Length
- Mean Diameter
- Branching Angle
- Spine Density
- Resistance
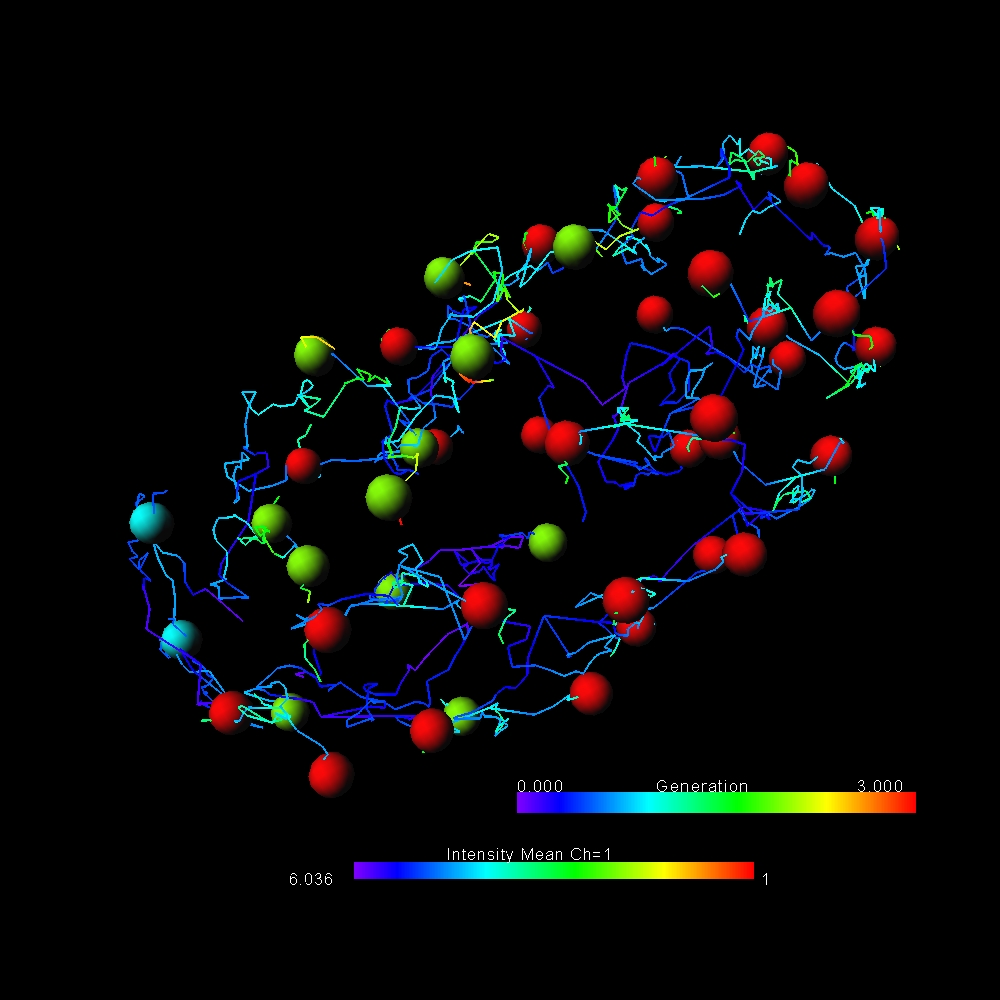
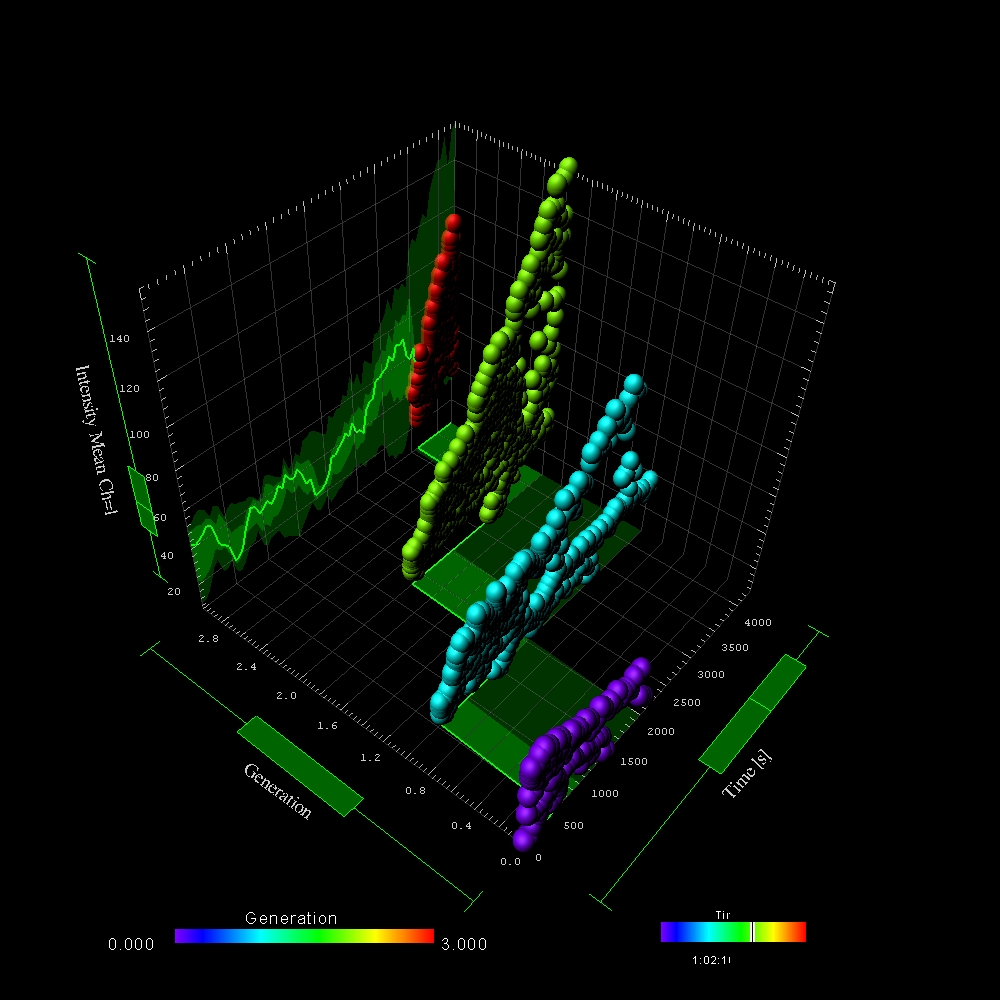
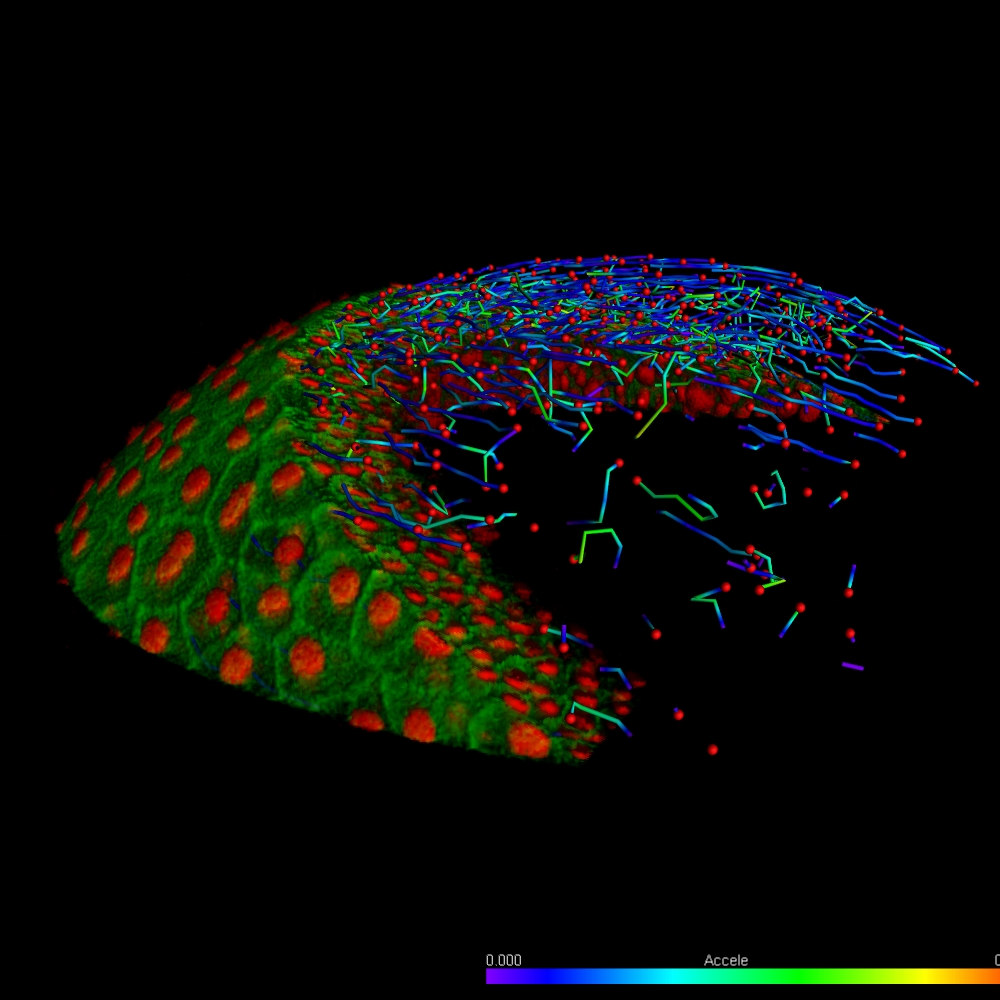
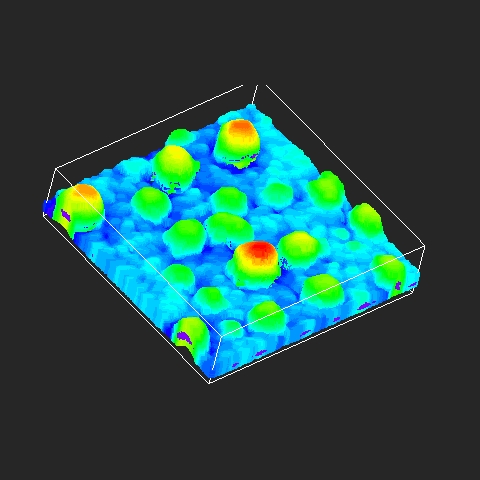
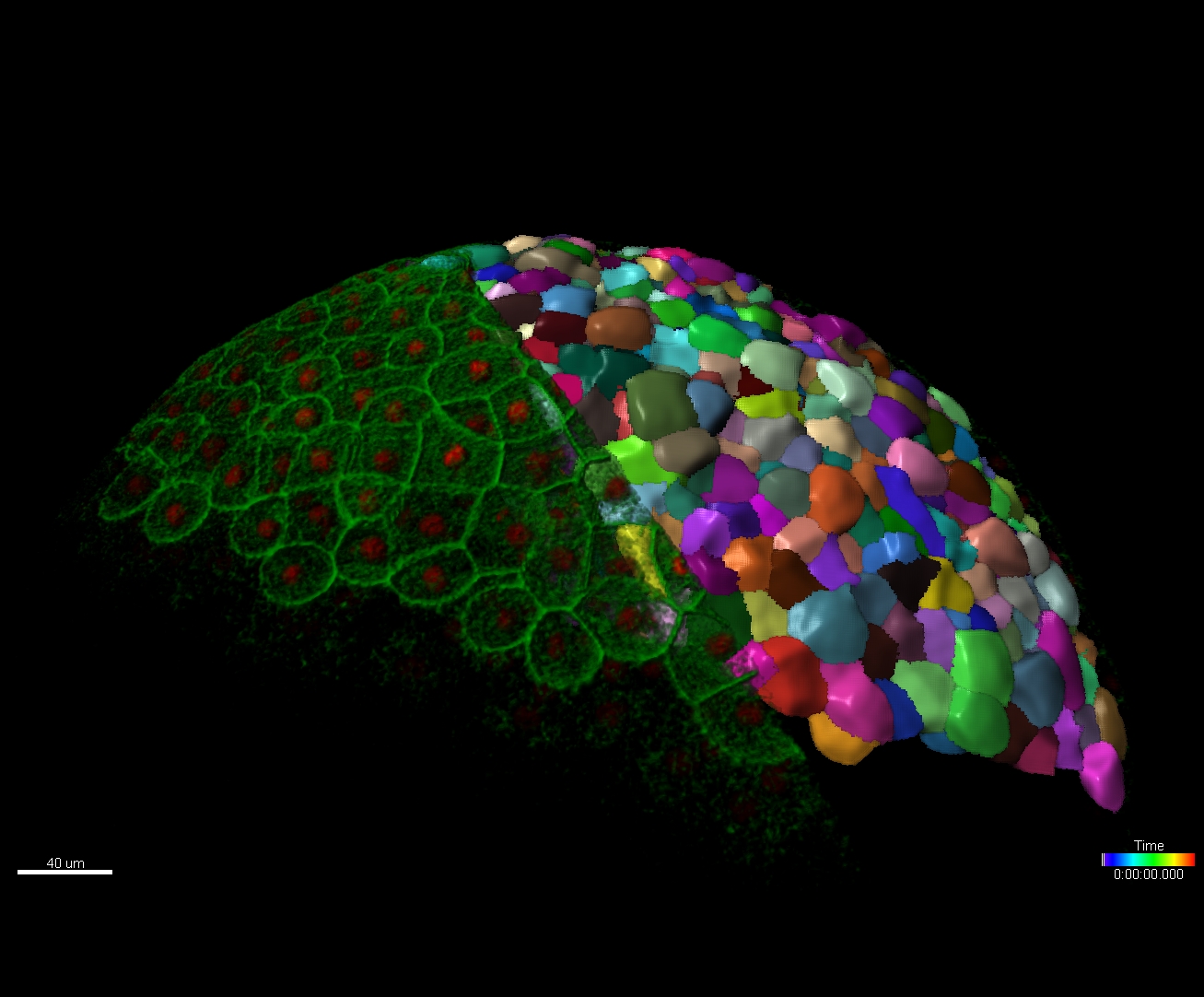
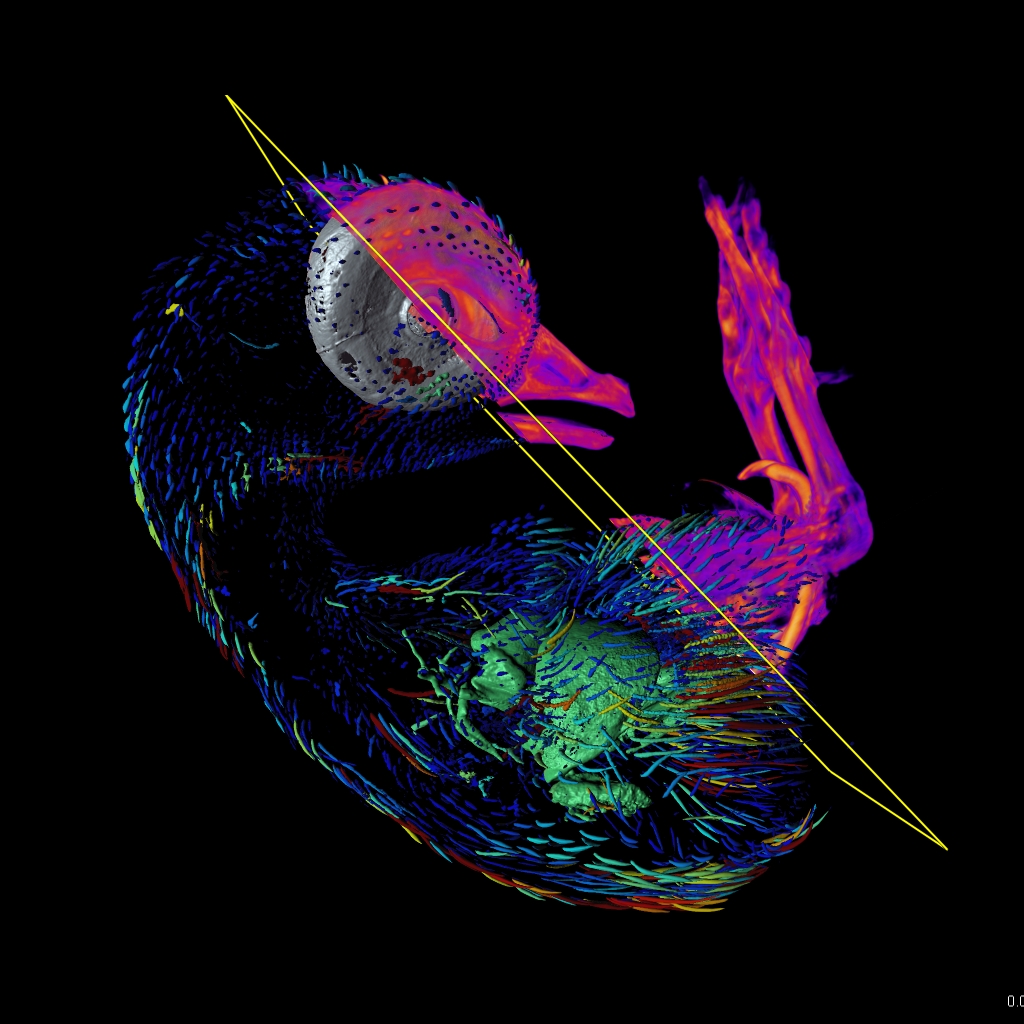
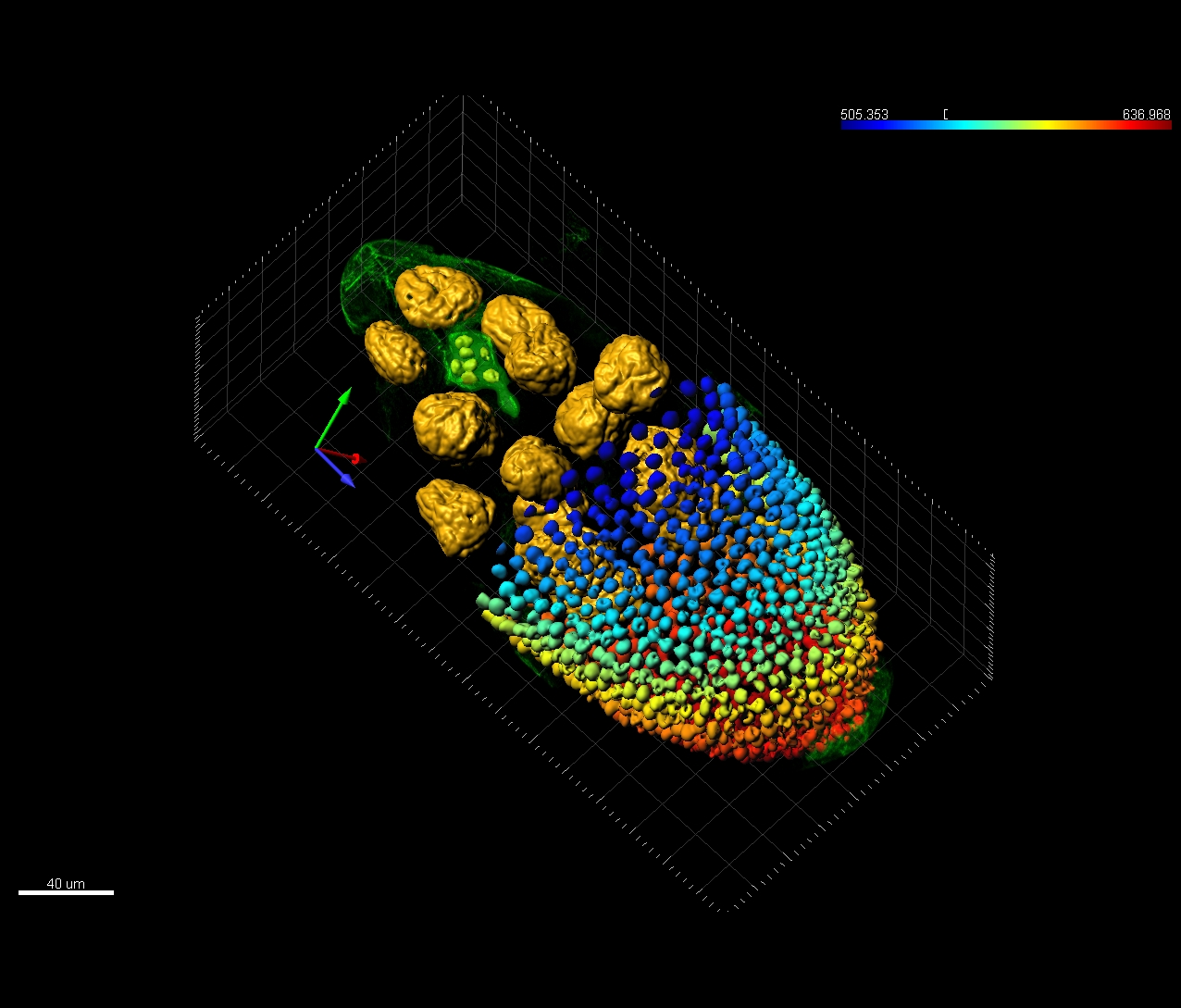
Imaris provides a complete set of features for visualization of multi-channel microscopy datasets from static 2D images to 3D time series regardless their size and format. Using Imaris for Neuroscientists users can:
The Imaris Learning Center hosts a wide range of tutorial videos, how-to articles and webinars to guide you through the many features of Imaris. We have provided some links below which will get you started on some of our most recent developments.

 公安机关备案号31010402003473
公安机关备案号31010402003473